Summary
– Since the food crisis of 2008, a considerable number of media reports have shed light on large-scale farmland acquisitions by foreign investors in developing countries, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa.
– While the media has essentially emphasized the role of foreign investors in land grabbing, other actors are actively involved in land acquisitions in African countries: local elites.
– Although land acquisitions by local elites are a phenomenon largely unknown to the public, empirical studies reveal that, like land grabbing by foreign investors, this type of land grabbing threatens vulnerable groups’ access to livelihood resources.
In recent years, there has been strong interest in large-scale acquisitions of farmland by foreign public or private investors in developing countries (see Cotula et al., 2009). With around 70 percent of land deals targeting African countries, the continent has been the most affected by this phenomenon since 2008. Friis and Reenberg (2010) estimate the amount of land affected by « land grabbing » in Africa to be between 51 and 63 million hectares, i.e., an area equivalent to the size of France. At the country level, countries such as the Democratic Republic of Congo and Mozambique are particularly affected by large-scale land acquisitions, which account for 49 percent and 21 percent of agricultural land respectively (for more details, see Friis and Reenberg (2010)). The key drivers of large-scale land acquisitions identified are high food prices and concerns about food and energy security (see Vermeulen and Cotula, 2010; Cotula, 2012 and references herein). The figures below show the distribution of publicly reported deals by region (Land Matrix database available on http://landmatrix.org/).
Figure 1: Land acquisitions by region, number of projects and size
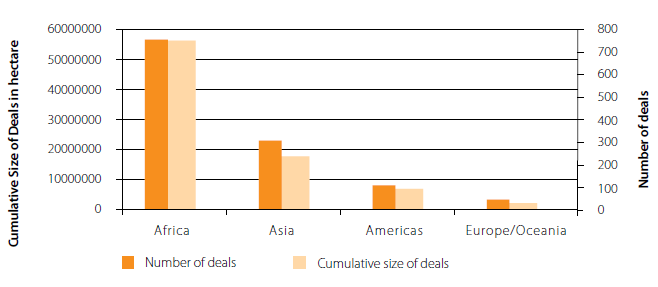
Source: Anseeuw et al. (2012), BSI Economics.
Concerns about land acquisitions by foreign investors
Although it remains difficult to have a clear picture of the land grab issue in Africa, several mediatized [1] land deals in Madagascar, Sudan, Mali, Ethiopia, Mozambique have contributed to draw attention of scholars, civil society, as well as development agencies on this issue (Cotula and Vermeulen, 2009; von Braun and Meinzen-Dick, 2009; Andrianirina–Ratsialonana et al., 2011, Deininger et al., 2011; Anseeuw et al., 2012, etc.). Thus, a growing body of literature on land grabbing is questioning the implications of land grabbing for agricultural production, infrastructure development, employment, and also for the livelihoods of poor rural households. Regarding the latter, results of case studies from Ethiopia, Mozambique, and Tanzania reported in Cotula et al. (2009) and Vermeulen and Cotula (2010) suggest an overall negative impact of land acquisitions on rural populations. This negative impact may be attributed to the fact that large-scale land acquisitions are responsible for smallholder loss of farmland. Indeed, the perceived land abundance in African countries that explains foreign investors’ interest in the continent hides another reality. Due to rapid population growth, urbanization and related changes in land use, as well as land degradation, farmland availability in African rural areas is increasingly difficult. Moreover, as noted by Cotula et al. (2009), the so-called « under-used lands » in African rural areas may be exploited by households for shifting cultivation or grazing. Thus, large-scale land acquisitions accentuate competition over land, especially as investors are often interested in high-value lands. Another important issue is the process of land acquisition by investors and especially the involvement of local populations in this process. It is noteworthy that a large majority of land in African rural areas is held under customary land law. As emphasized by Vermeulen and Cotula (2010), while in many African countries local populations’ land rights (principally use rights) are acknowledged within formal law, they are « not necessarily protected. » The authors also note that no African country confers the right on local populations to prevent land from being attributed to investors by government agencies in particular. However, as stated by the authors, in countries such as Ghana, Mozambique, and Tanzania, local populations affected by land deals are involved in the land acquisition process. For instance,“land transfers must be approved by the communities or customary leaders that have rights over the land in question”(Vermeulen and Cotula, 2010). While this is a step toward greater inclusion of local populations in the land acquisition process, it also raises the issue of vulnerable groups such as women, migrants, and pastoralists. Indeed, those groups, which are the most likely to lose access to land, are often excluded from decision-making processes for the approval of land deals by local communities. This situation may be explained by the fact that, due to relatively low bargaining power, those groups already suffer from restrictions in access to and use rights over land (see, for example, de Schutter, 2011).
Land acquisitions by African elites: a gap in the literature?
While media reports on land grabbing have helped raise public awareness about the potential consequences of land grabbing by foreign investors in Africa, land acquisitions by local elites remain a largely unknown phenomenon [2]. Moreover, the existing literature on land grabbing in Africa mainly emphasizes land acquisitions by foreign public or private investors. However, as pointed out by several empirical studies, land acquisitions and related dispossession of smallholder farmers in countries such as Benin, Burkina Faso, or Nigeria may be essentially attributed to local investors. As stated by the World Bank, local investors account for at least 50 percent of land acquisitions in Ethiopia, Mozambique, and Sudan. Moreover, figures for Nigeria show that local investors acquired 90 percent of the area allocated in the country (see Deininger et al., 2011) [3]. While these figures must be taken with caution as local investors may act on behalf of foreigners, they contribute to shedding light on a phenomenon that threatens the livelihoods and food security of rural households, particularly vulnerable groups of people, in several African countries. Moreover, other empirical findings, particularly in African peri-urban areas, confirm the increase in land sale market activities due to land demand from urban elites (see, for example, Benjaminsen and Sjaastad, 2002). However, it is worth noting that the phenomenon of land acquisitions by national investors is not restricted to peri-urban areas. Indeed, empirical studies in West and Southern African rural areas suggest that land acquisitions by civil servants, government officials, or businessmen are responsible, inter alia, for a rapid decrease in land reserves in some localities. As in the case of land acquisitions by foreign investors, the related increase in pressure on land has further implications for women and migrants [4], whose access to land is being reduced (Zongo and Mathieu, 2000; Hilhorst, 2011).
In addition to livelihoods considerations, it should be stressed that, regardless of whether it involves national elites or foreign investors, land grabbing further raises questions about the future of smallholder agriculture and the increase in agricultural productivity. If the success of large farms in countries like Brazil is a plea to foster large mechanized farms in African countries, empirical evidence in African countries showed the poverty reduction role of small farms as well as large farms failures to promote agricultural and rural development (see Binswanger et al., 1995; Diao et al., 2010). Therefore, regarding the latter, a good step toward agricultural and rural development in Sub-Saharan Africa could be the redefinition of existing land and rural policies.
Remarks
[1] See Friis and Reenberg (2010) and the online database by GRAIN (farmlandgrab.org) for media reports on land deals.
[2] As mentioned by Cotula (2012), this situation may be explained by the lack of attention paid by the media to deals involving national investors.
[3] Statistics are drawn from the inventory data for the period 2004-2009 that have been collected for the study.
[4] We should keep in mind that the « migrants » category is not homogenous. Indeed, several studies in the African context have shown that better-off migrants may contribute to women and « poor » migrants’ loss of access to land (see Dabiré and Zongo, 2005).
References
– R. Andrianirina-Ratsialonana, L. Ramarojohn, P. Burnod, and A. Teyssier. After Daewoo? Current status and perspectives of large scale land acquisitions in Madagascar. Commercial pressures on land studies, International Land Coalition (ILC), 2011.
– W. Anseeuw, M. Boche, T. Breu, M. Giger, J. Lay, P. Messerli, and K. Nolte. Transnational land deals for agriculture in the global south: Analytical report based on the land matrix database. Technical report, CDE/CIRAD/GIGA, 2012.
– T. A. Benjaminsen and E. Sjaastad. Race for the prize: Land transactions and rent appropriation in the Malian cotton zone. European Journal of Development Research, 14(2):129–152, 2002.
– H. P. Binswanger, K. W. Deininger, and G. Feder. Power, distortions, revolt and reform in agricultural land relations. In H. Chenery and T. Srinivasan, editors, Handbook of Development Economics, volume 3, Part 2, chapter 42, pages 2659–2772. Elsevier, 1 edition, 1995.
– L. Cotula. Land Grab Or Development Opportunity? Agricultural Investment and International Land Deals in Africa. IIED, 2009.
– L. Cotula. The international political economy of the global land rush: A critical appraisal of trends, scale, geography and drivers. Journal of Peasant Studies, 39(3-4):649–680, 2012.
– L. Cotula and S. Vermeulen. Deal or no deal: the outlook for agricultural land investment in Africa. International Affairs, 85(6):1233–1247, 2009.
– B. Dabiré and M. Zongo. The impact of the Ivorian crisis on access to land in Comoé province. Technical report, International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED), 2005.
– O. de Schutter. The green rush: the global race for farmland and the rights of land users. Harvard International Law Journal, 52:503–559, 2011.
– K. Deininger, D. Byerlee, J. Lindsay, A. Norton, H. Selod, and M. Stickler. Rising Global Interest in Farmland: Can it Yield Sustainable and Equitable Benefits? Number 2263 in World Bank Publications. The World Bank, September 2011.
– X. Diao, P. Hazell, and J. Thurlow. The role of agriculture in African development. World Development, 38(10):1375–1383, 2010.
– C. Friis and A. Reenberg. Land grab in Africa: Emerging land system drivers in a teleconnected world. GLP Reports 1, GLP International Project Office, 2010.
– T. Hilhorst, J. Nelen, and N. Traoré. Agrarian change below the radar screen: Rising farmland acquisitions by domestic investors in West Africa. Results from a survey in Benin, Burkina Faso and Niger. Paper presented at the International Conference on Global Land Grabbing 6-8 April 2011, 2011.
– S. Vermeulen and L. Cotula. Over the heads of local people: consultation, consent, and recompense in large-scale land deals for biofuels projects in Africa. Journal of Peasant Studies, 37(4):899–916, 2010.
– J. von Braun and R. S. Meinzen-Dick. « Land grabbing » by foreign investors in developing countries: Risks and opportunities. Policy briefs 13, International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), 2009.
– M. Zongo and P. Mathieu. Commercial land transactions in western Burkina Faso: vulnerability, conflicts, security, insecurity. APAD Bulletin, 19, 2000.